Oracle Archive Manager: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
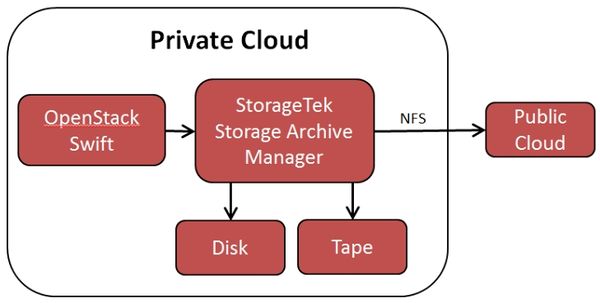
Objects are created using OpenStack Swift and passed into the StorageTek Storage Archive Manager System. These objects are then stored in the StorageTek QFS filesystem. When QFS receives the object it is stored using an |
Objects are created using OpenStack Swift and passed into the StorageTek Storage Archive Manager System. These objects are then stored in the StorageTek QFS filesystem. When QFS receives the object it is stored using an |
||
MD5 hash generated by the Swift proxy which becomes the filename within the QFS filesystem. When an object is retrieved, Swift will generate the hash to identify which file to read within the QFS file system. Because of this system of converting account, container and object names into unique hashes, no central database of the object locations is required. The same hash is generated each time an object is written or accessed. Within StorageTek Storage Archive Manager policies determine how many copies of the object are created and which type of storage device each copy resides on. |
MD5 hash generated by the Swift proxy which becomes the filename within the QFS filesystem. When an object is retrieved, Swift will generate the hash to identify which file to read within the QFS file system. Because of this system of converting account, container and object names into unique hashes, no central database of the object locations is required. The same hash is generated each time an object is written or accessed. Within StorageTek Storage Archive Manager policies determine how many copies of the object are created and which type of storage device each copy resides on. |
||
[[File:oracle_archive_manager.jpg|center|600px|caption]] |
|||
One of the features of OpenStack Swift is the automatic auditing of stored objects. When used with StorageTek Storage Archive Manager this auditing is suppressed, because StorageTek Storage Archive Manager performs its own data integrity validation audits automatically and independently of Swift. If a data integrity issue is found, then StorageTek Storage Archive Manager can be configured to self heal and create new copies of the corrupted data automatically. By not using the Swift audit process, continuous recalls from tape are avoided. |
One of the features of OpenStack Swift is the automatic auditing of stored objects. When used with StorageTek Storage Archive Manager this auditing is suppressed, because StorageTek Storage Archive Manager performs its own data integrity validation audits automatically and independently of Swift. If a data integrity issue is found, then StorageTek Storage Archive Manager can be configured to self heal and create new copies of the corrupted data automatically. By not using the Swift audit process, continuous recalls from tape are avoided. |
||
Latest revision as of 21:19, 17 October 2014
This description is taken from one of the product briefs:
The OpenStack Swift interface enables a StorageTek QFS Client server to be used as a Swift storage node. OpenStack Swift storage environments typically have several storage nodes, and data is then replicated and stored on multiple nodes (usually 3). With StorageTek Storage Archive Manager, it creates copies of data on disk and digital tape devices independently of Swift. Therefore a typical implementation of this solution will write a single copy of an object to a storage node and QFS will create multiple copies of the object on disk or tape. Each storage node will be a separate StorageTek QFS Client.
Objects are created using OpenStack Swift and passed into the StorageTek Storage Archive Manager System. These objects are then stored in the StorageTek QFS filesystem. When QFS receives the object it is stored using an MD5 hash generated by the Swift proxy which becomes the filename within the QFS filesystem. When an object is retrieved, Swift will generate the hash to identify which file to read within the QFS file system. Because of this system of converting account, container and object names into unique hashes, no central database of the object locations is required. The same hash is generated each time an object is written or accessed. Within StorageTek Storage Archive Manager policies determine how many copies of the object are created and which type of storage device each copy resides on.
One of the features of OpenStack Swift is the automatic auditing of stored objects. When used with StorageTek Storage Archive Manager this auditing is suppressed, because StorageTek Storage Archive Manager performs its own data integrity validation audits automatically and independently of Swift. If a data integrity issue is found, then StorageTek Storage Archive Manager can be configured to self heal and create new copies of the corrupted data automatically. By not using the Swift audit process, continuous recalls from tape are avoided.